Development of an Analytical Framework for Reverse Logistics Supply Chain in Industrial Waste Management Based on Grounded Theory and Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM)
Keywords:
Reverse logistics supply chain, industrial waste, gas refining industry, grounded theory, interpretive structural modeling (ISM)Abstract
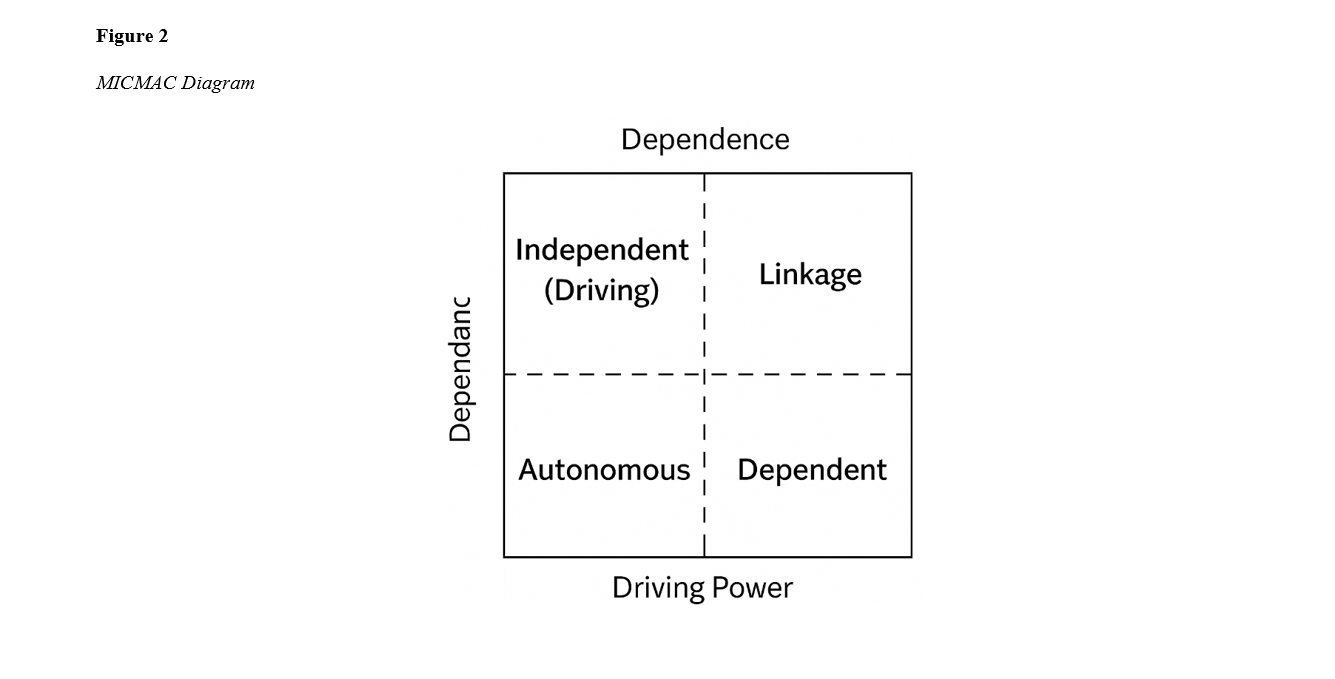
The rapid growth of technology and the emergence of new production processes, along with the substitution of synthetic materials and chemical compounds, have resulted in an increased volume of industrial waste and, in some cases, the generation of hazardous waste. Improper handling, transportation, and disposal of this waste, part of which contains dangerous substances, pose serious challenges to human health and the environment. Under such circumstances, establishing an efficient reverse logistics network emerges as an inevitable necessity. With growing social concerns about environmental issues, reverse logistics has become increasingly integrated with waste management, and the management of industrial waste is now considered a core pillar of reverse supply chain management. This study, employing the grounded theory method based on the Strauss and Corbin (1998) model and using the insights of 17 academic and industrial experts in the national gas refining sector, proposes a comprehensive model for the reverse supply chain of waste in this industry. The analysis of data obtained from semi-structured interviews led to the identification of 25 core concepts categorized into six main themes. The application of Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) revealed hierarchical and causal relationships among these factors, indicating that regulations and policies, infrastructure, and organizational culture act as fundamental and driving forces with the greatest impact on the success of the system. This paradigmatic model can serve as a roadmap for managers in the gas refining industry to design and implement an effective and sustainable reverse logistics system.
References
Aghaeipour, Y., & Pirdasht, M. (2022). Presentation and Solution of a Reverse Supply Chain Location Model for Collecting End-of-Life Vehicles Considering Sustainability Dimensions and Metaheuristic Algorithms. https://www.noormags.ir/view/en/articlepage/1967721/
Alimi, I., Azar, A., & Ghafari, F. (2022). Dynamics of Knowledge Management Behavior on Supply Chain Transportation and Logistics Based on System Dynamics Methodology (SD). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137650
Gharaakhani, D. (2022). Identification and Ranking of Barriers Affecting the Implementation of Reverse Logistics in the Automotive Industry Using Fuzzy ANP and DEMATEL Techniques. Third International Conference on Management and Industry,
Ghazifard, A. K., & Rasouli, K. (2021). Study of Influential Variables on Reverse Logistics and Closed-Loop Supply Chain in the Oil and Gas Industry of Gachsaran Using Hierarchical Methods. Seventh International Conference on Management and Accounting Sciences,
Guarnieri, P., Streit, J. A. C., & Batista, L. (2020). Reverse Logistics and the Sectoral Agreement of Packaging Industry in Brazil Towards a Transition to Circular Economy. Resources Conservation and Recycling, 153, 104541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.104541
Hsin, R., Syarif Daniel, B., Charlotte, N. M., Astrow, A., Anslem, J., & Corbin, J. J. (2023). Improving the sustainability of a reverse supply chain system under demand uncertainty byHere are the provided references formatted in RIS format: ```ris Foundations of Qualitative Research: Techniques and Stages of Grounded Theory Production. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0956053X21003007
Islampanah, A., Jafarnejad Chaghooshi, A., Heydari Dehuyi, J., & Taghizadeh Yazdi, M. R. (2023). Designing a Reverse Supply Chain Network for Industrial Waste Using Intelligent Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication Systems (VANET): A Case Study of the Iranian Automotive Industry. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137650
Jafari, P., Fahiminasab, A., Marsal, B., & Tayebi Sani, S. M. (2020). Studying the Barriers Affecting the Formation of Reverse Logistics in Sports Events. https://www.noormags.ir/view/en/articlepage/1714879
Khosravi, M. R., Homayi, R., & Hoorali, M. (2019). Designing a Conceptual Model for Reverse Logistics Management Network with an Innovation Supply Chain Approach. Innovation and Value Creation, 8(16), 1-15. https://www.sid.ir/paper/368423/
Kouchaki Tajani, E., Ghaneh Kani, A., Daneshmandmehr, M., & Hosinzadeh, A. A. (2022). Designing a Robust Sustainable Agile Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network with Different Sales Channels. Journal of Decision Making and Operations Research, 7(1). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360835222007367
Lal bar, A., & Hassani, M. (2022). Managerial ability, political connections and fraudulent financial reporting. Interdisciplinary Studies on Strategic Knowledge, 5(20), 141-162. https://issk.sndu.ac.ir/article_1783_bbda64a11fc132079762aa7477e4700e.pdf
Meilenda, P., & Syarif, A. (2024). Reverse Logistics Analysis of Chips Products Towards Green Supply Chain Management in MSMEs. Sinergi International Journal of Management and Business. https://doi.org/10.61194/ijmb.v2i4.230
Miraghaei, S. S. (2020). The Impact of Integrated Reverse Logistics on the Green Supply Chain with Emphasis on Environmental Factors. First Conference on Industrial Engineering, Economics, and Management,
Mohghar, A., Mansouri, T., & Hadadi, S. (2024). A Model for Outsourcing Reverse Logistics Planning Based on Fuzzy-Intuitive Analysis Considering Artificial Intelligence Methods. Perspective of Industrial Management, 14(2), 136-152. https://civilica.com/doc/2017727/
Mugoni, E., Nyagadza, B., & Hove, P. K. (2023). Green reverse logistics technology impact on agricultural entrepreneurial marketing firms' operational efficiency and sustainable competitive advantage. Sustainable Technology and Entrepreneurship, 2(2), 100034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stae.2022.100034
Neha, S., Biswajit, S., Hui-Ming, W., Samuel, R., Singh, S. R., & Hsiao, Y. L. (2023). A reverse logistics model with eco-design under the Stackelberg-Nash equilibrium and centralized framework. 387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135789
Qazi Far, A. K., & Rasouli, K. (2021). Study of influential variables on reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain in the oil and gas industry of Gachsaran using hierarchical methods. Seventh International Conference on Management and Accounting Sciences, Tehran.
Singh, A., Goel, A., Chauhan, A., & Singh, S. K. (2025). Sustainability of electronic product manufacturing through e-waste management and reverse logistics. Sustainable Futures, 9(3), 77-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2025.100490
Taheri, M. T., Makial Aghae, M., & Samadyar, H. (2022). Prioritization and Management of Industrial Waste at the Ninth Refinery of South Pars Gas Complex. Environmental Science and Water Engineering, 8(4), 842-855. https://www.jewe.ir/article_146971.html
Tavakoli, N., Sharifi, M., Khanali, M., & Ghasemi Mobtaker, H. (2023). Evaluation and Design of a Forward-Reverse Logistics Supply Chain Network for the Shiraz Biogas Power Plant. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14137650
Vaez, N., & Shahbazi Chagani, Z. (2022). Network Analysis of Barriers to Establishing Reverse Logistics in Cellulose Industries of Saveh County. First International Conference on Research in Accounting, Management, Economics, and Humanities,
Yu, H., Sun, X., Solvang, W. D., & Zhao, X. (2020a). Reverse Logistics Network Design for Effective Management of Medical Waste in Epidemic Outbreaks: Insights from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in Wuhan (China). International journal of environmental research and public health, 17, 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051770
Yu, H., Sun, X., Solvang, W. D., & Zhao, X. (2020b). Reverse Logistics Network Design for Effective Management of Medical Waste in Epidemic Outbreaks: Insights from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in Wuhan (China). International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(1770). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051770
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zahra Ramezani (Author); Sadegh Feizollahi; Maryam Daneshmand Mehr (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









