Providing a Digital Supply Chain Model in the Online Food Retail Industry
Keywords:
Digital supply chain, Retail, Online food supermarketAbstract
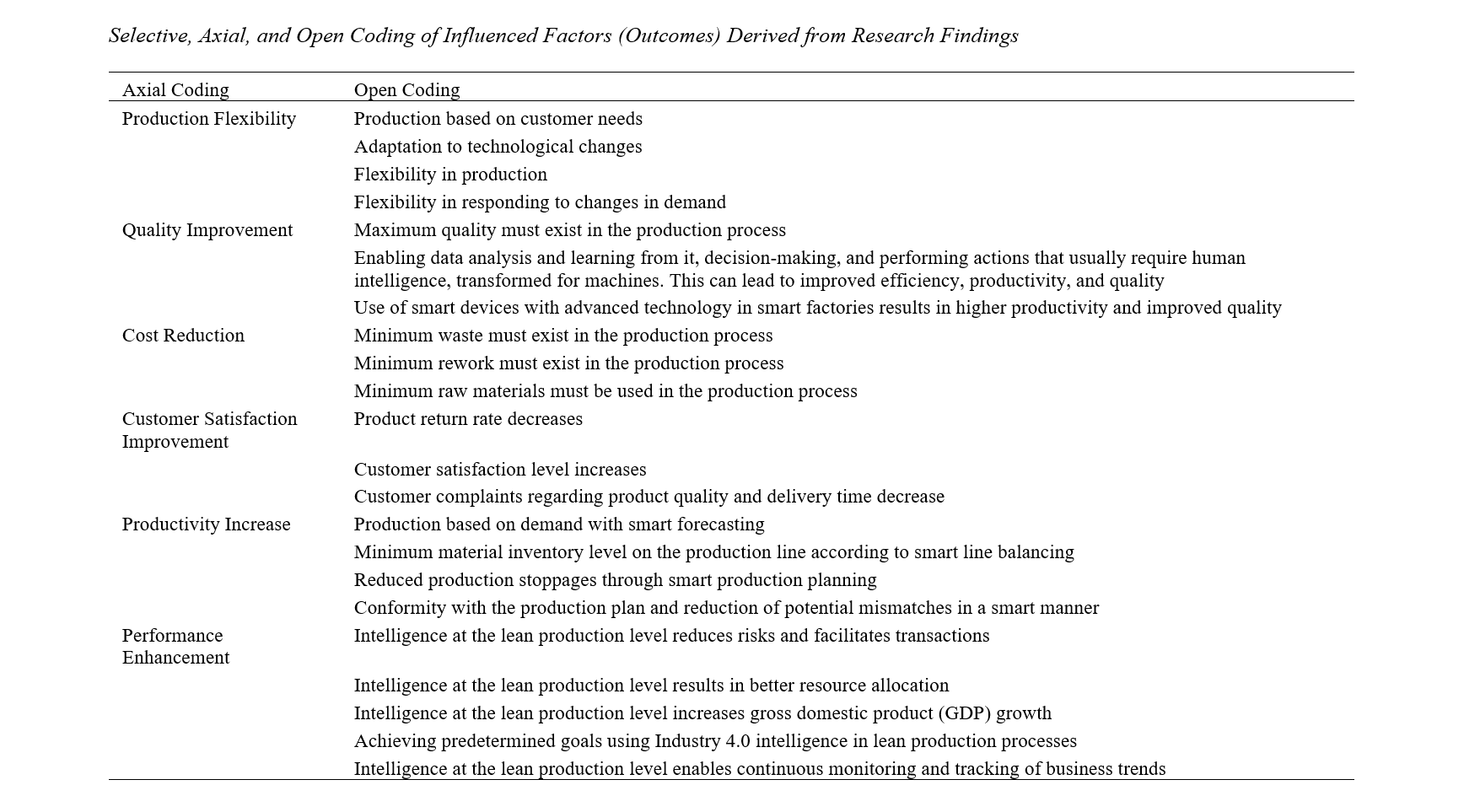
This study was conducted with the aim of presenting a digital supply chain model in the online food retail industry. In terms of purpose, it is applied research, and in terms of data collection, it falls under mixed-method studies (qualitative–quantitative). The statistical population in the qualitative section consisted of professors, experts in the field of technology and supply chain, as well as senior managers of production and research and development in the online food retail industries. In the quantitative section, the population included all managers and employees of online supermarkets in Tehran. The sample size in the qualitative section was determined based on theoretical saturation (10 participants) using purposive sampling, while in the quantitative section, it was estimated at 380 participants based on structural equation modeling sampling requirements, using stratified random sampling. The data collection tool in the qualitative section was interviews, and in the quantitative section, a researcher-made questionnaire. The validity of the questionnaire was confirmed in terms of face and content validity by several experts; convergent validity was verified through the calculation of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE), and discriminant validity was confirmed using the square root of AVE. The reliability of the questionnaire was obtained through Cronbach’s alpha at 0.898 for the entire instrument. SmartPLS 3 software was used for data analysis. The findings led to the identification of 27 components and 106 indicators. The variables of smart customer relationship management, intelligent communication in the supply chain, smart inventory and warehouse management, smart production control, and smart maintenance were identified as the main effective categories. Economic, social, technological, environmental, managerial, organizational, and industrial factors were identified as the effective causal conditions. Employee knowledge and skills, employee intelligence and awareness, and appropriate infrastructure were recognized as effective contextual conditions. Intra-organizational factors, laws and regulations, and inter-organizational factors were considered as effective intervening conditions. Financing, employee empowerment, and cultural development for creating a smart supply chain were determined as effective strategies. Finally, the outcomes included cost reduction, quality improvement, productivity increase, performance enhancement, flexibility, and customer satisfaction improvement.
References
Ahmad, N. R. (2025). Exploring the Role of Digital Technologies in Enhancing Supply Chain Efficiency: A Case Study of E-Commerce Companies. Indus Journal of Social Sciences, 3(1), 226-237. https://doi.org/10.59075/ijss.v3i1.618
Bagheri, N., Haddadi Herandi, A. A., & Valmohammadi, C. (2021). Identifying and Prioritizing Digital Transformation Maturity Dimensions in the Food Industry with a Fuzzy DANP Approach. Encyclopedia of Digital Transformation, 2(3), 1-27. https://dtj.mehralborz.ac.ir/article_175289_en.html
Burgos, D., & Ivanov, D. (2021). Food retail supply chain resilience and the COVID-19 pandemic: A digital twin-based impact analysis and improvement directions. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 152, 102412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2021.102412
Dias, D. O., Marin, J. M. M., & Fuentes, J. M. (2022). The link between information and digital technologies of industry 4.0 and agile supply chain: Mapping current research and establishing new research avenues. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 167, 108000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2022.108000
Duan, Y., Khokhar, M., Raza, A., Sharma, A., & Islam, T. (2025). The role of digital technology and environmental sustainability in circular supply chains based on the fuzzy TOPSIS model. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 1-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-024-05924-4
El Bhilat, E. M., & Hamidi, L. S. (2025). Achieving efficiency and sustainability in digital retail supply chains: a systematic literature review and research agenda. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJPPM-07-2024-0486/full/html
Evdokimova, E. N., Kupriyanova, M. V., Solovyova, I. P., & Simikova, I. P. (2023). Enablers and Barriers of Digital Transformations Industry: A Study of Regional Development. In V. I. Trukhachev (Ed.), Unlocking Digital Transformation of Agricultural Enterprises. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-13913-0_11
Gagliardi, A. R., Festa, G., Usai, A., Dell'Anno, D., & Rossi, M. (2023). The impact of knowledge management on the digital supply chain-a bibliometric literature review. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-07-2022-0206
Haryanti, T., Rakhmawati, N. A., & Subriadi, A. P. (2023). The Extended Digital Maturity Model. Big Data and Cognitive Computing, 7(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc7010017
Hassanpour, H. A., Taheri, S. M. R., & Mikaeli, F. (2021). Designing a Food Supply Chain Network Based on Customer Satisfaction Under Uncertainty Conditions. Business Management Explorations, 13(26), 395-431. https://bar.yazd.ac.ir/article_2612.html?lang=en
Hossein Khani, M., Heydarieh, S. A., Faezi Razi, F., & Hashemi Tilehnoui, M. (2022). Simulation of Agile and Smart Supply Chain Integration in the Iranian Health Industry Using a System Dynamics Approach. Management, 3(3), 212-223. https://asm.pgu.ac.ir/article_705454_en.html
Jantrani, A., Barati, M., Ghobakhloo, M., Shaheen, A., & Talari, M. (2022). Identifying the Requirements for Implementing the Industrial Internet of Things in the Automotive Industry Supply Chain. Operations Management, 2(7), 27-54. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/369230207_Identifying_the_requirements_of_using_the_Industrial_Internet_of_Things_in_the_automotive_supply_chain
Jin, H., & Wang, Z. (2025). A Review of Research on the Impact of the Digital Economy on Automotive Supply Chain Resilience. https://doi.org/10.3233/faia250011
Kayikci, Y., Subramanian, N., Dora, M., & Bhatia, M. S. (2022). Food supply chain in the era of Industry 4.0: Blockchain technology implementation opportunities and impediments from the perspective of people, process, performance, and technology. Production Planning & Control, 33(2-3), 301-321. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2020.1810757
Kurdi, B., Alzoubi, H., Akour, I., & Alshurideh, M. (2022). The effect of blockchain and smart inventory system on supply chain performance: Empirical evidence from retail industry. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 10(4), 1111-1116. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2022.9.001
Mehdipour, P., Safaei Ghadikolaei, A. H., Fallah Lajimi, H. R., & Aghajani, H. A. (2022). Measuring the Digital Supply Chain in Manufacturing Industries (Case Study: Sleep Goods Industry). Management Research in Iran, 26(1), 139-163. https://mri.modares.ac.ir/article_587.html?lang=en
Mohammadi, J. (2023). What is a Digital Supply Chain and What are its Advantages? https://podro.com/blog/digital-supply-chain/
Najjar, M., & Yasin, M. M. (2021). The management of global multi-tier sustainable supply chains: a complexity theory perspective. International Journal of Production Research. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2021.1990432
Nozari, H., Sadeghi, M. E., Ghahramani Nahar, J., & Najafi, S. E. (2021). Quantitative Analysis of Challenges in Implementing Digital Supply Chain Based on Internet of Things Technology (Supply Chain 4.0). Scientific Quarterly of Standard and Quality Management, 11(3), 63-94. https://www.jstandardization.ir/article_148441.html
Rahamneh, A., Alrawashdeh, S., Bawaneh, A., Alatyat, Z., Mohammad, A., & Al-Hawary, S. (2023). The effect of digital supply chain on lean manufacturing: A structural equation modelling approach. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 11(1), 391-402. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.uscm.2022.9.003
Rahimi, A., Taghizadeh, G., & Mahmoodabadi, S. (2022). Presenting an Interpretive Structural Model of Barriers to Blockchain Technology Adoption in the Food Industry Supply Chain. Production and Operations Management Research, 13(1), 79-104. https://doi.org/10.1080/21693277.2022.2120420
Roknoddini, S. A. R., Andaleeb Ardakani, D., Zare Ahmadabadi, H., & Hosseini Bamakan, S. M. (2023). Modeling Industry 4.0 Enablers in Implementing a Sustainable Supply Chain Using a Fuzzy DEMATEL-ANP Approach. Industrial Management Perspective, 13(1), 141-172. https://jimp.sbu.ac.ir/article_103168.html?lang=en
Salimi Zavieh, S. G., & Shams, S. (2023). Analysis of Digital Supply Chain Management (Future Development Trend). Iran Rubber Industry, 25(102), 49-62. https://www.magiran.com/paper/2319501/digital-supply-chain-management-analysis-future-development-trend?lang=en
Shahabi, V., Azar, A., Faezi Razi, F., & Fallah Shams, M. F. (2022). Analysis of Factors Affecting the Development of Banking Service Supply Chains in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. Management Research in Iran, 26(2), 95-114. https://mri.modares.ac.ir/article_578.html?lang=en
Shevtshenko, E., Maas, R., Murumaa, L., Karaulova, T., Raji, I. O., & Popell, J. (2022). Digitalisation of supply chain management system for customer quality service improvement. Journal of Machine Engineering, 22. https://doi.org/10.36897/jme/147803
Yu, Y. (2025). The Impact of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Resilience in Manufacturing: The Mediating Role of Supply Chain Integration. Sustainability, 17(9), 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093873
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hossein Samadi Vik (Author); Rasoul Sanavifard; Mostafa Khajeh (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









