Designing a Lean–World-Class Model in Electric Power Distribution
Keywords:
Model design, lean production, energy losses, loss reduction, electric power distribution, ; distribution automation, smart grid, continuous improvement in electricity distribution, world-class approachAbstract
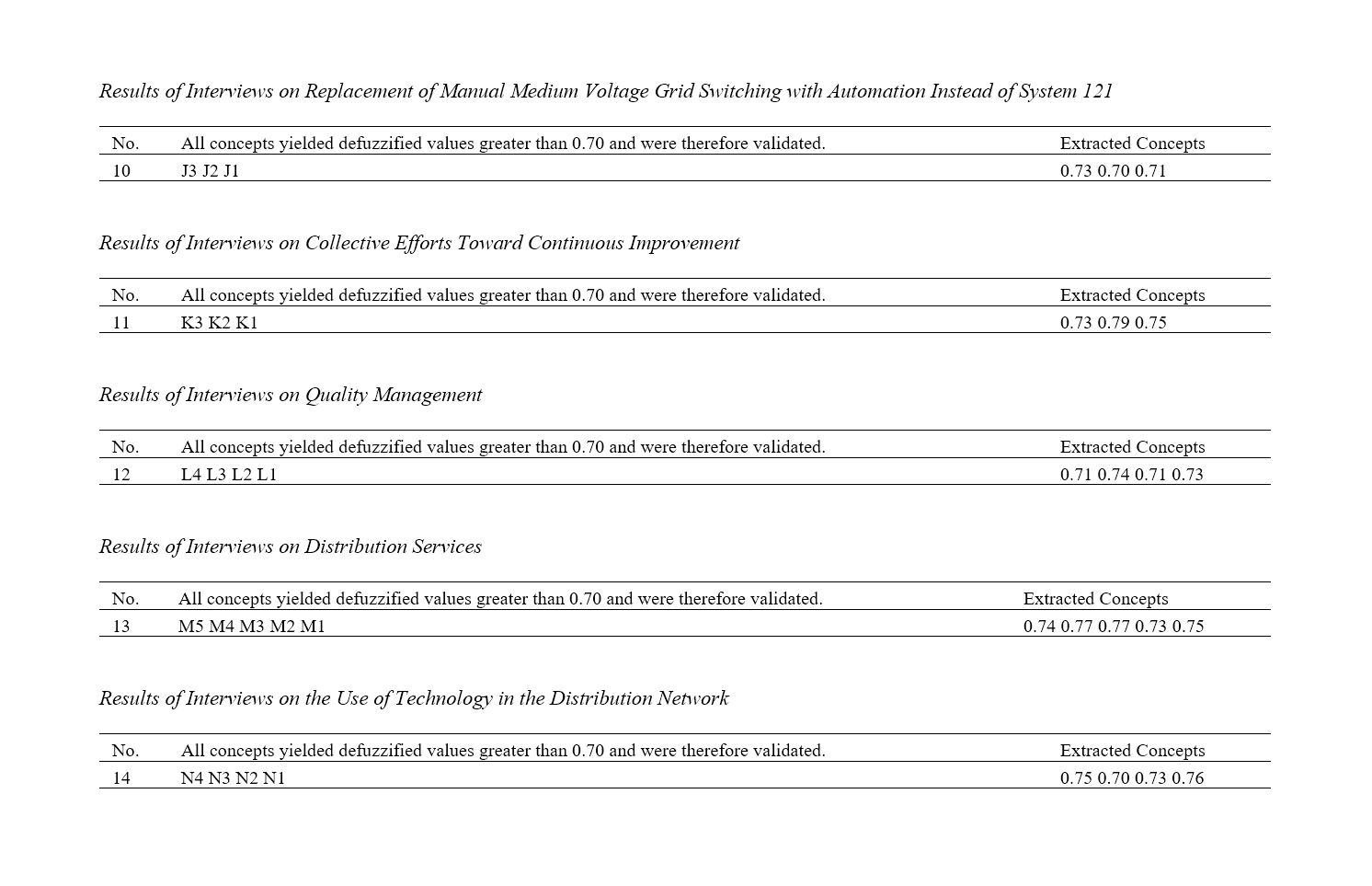
The primary objective of this study is to design a lean–world-class model in electric power distribution to evaluate the efficiency of Iran's electricity distribution chain, with the aim of improving the reliability and service quality of the electric power distribution network. Fuzzy logic-based methods enable the mathematical formulation of vague concepts and prediction. A comprehensive literature review was conducted to identify key indicators influencing lean and world-class production in electric power distribution. Face-to-face interviews were conducted, in line with the sample size required for each research method, with managers and experts at the Tehran Electricity Distribution Company. Fourteen indicators were identified, and through the fuzzy Delphi method, the extent to which Iran’s electricity distribution industry aligns with lean principles and world-class standards was assessed. In this qualitative study, the snowball sampling method was applied. The sample consisted of 26 specialists and experts. After interviewing these 26 experts from fields such as consumption management, customer services, Tehran electricity distribution dispatching, operation, and preventive maintenance (PM), 14 indicators were identified under the theme of "Designing a Lean–World-Class Model in Electric Power Distribution." Additionally, 54 concepts were extracted from the interview content and the body of existing literature and academic articles. The gender distribution among the experts interviewed comprised 12 women and 14 men, of whom 18 held master's degrees and 8 held doctorates. Through the fuzzy Delphi method and by identifying 14 key indicators and their associated concepts, this study evaluates the lean and world-class attributes of electricity distribution. It concludes that the designed lean–world-class model, with indicators such as loss reduction, value creation, enhanced reliability, and service quality in the distribution network, can significantly contribute to improving the efficiency of the electricity distribution chain in Iran.
References
Ahmadi, M., Zakerian, S. A., Salmanzadeh, H., & Mortezapour, A. (2016). Identification of the ergonomic interventions' goals from the viewpoint of ergonomics experts of Iran using Fuzzy Delphi Method. International Journal of Occupational Hygiene, 8(3), 151-157. https://ijoh.tums.ac.ir/index.php/ijoh/article/view/218
Asiyachi, M. (2024). World-class management. Sepehr Economy Journal of Kerman, 184-187. https://www.noormags.ir/view/fa/articlepage/2261545/
Fallahi, A., Fallahi, F. A. U. S. H., Ghaderi, S. F., & Ebrahimi, R. (2019). Application of a robust data envelopment analysis model for performance evaluation of electricity distribution companies. International Journal of Energy Sector Management, 15(4), 724-742. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-08-2018-0008
Ghaem Maghami, M. S., Asghari Zadeh, I., & Farsijani, H. (2022). Designing a performance evaluation model with a sustainable production approach in the global automotive industry. journal of Production and Operations Management, 13(3), 77-98. https://jpom.ui.ac.ir/article_26875.html
Habibi, A., & Adanvar, M. (2017). Structural equation modeling and factor analysis (Practical training of LISREL software). Jihad University Publishing Organization.
Habibi, A., Jahantigh, F. F., & Sarafrazi, A. (2015). Fuzzy Delphi technique for forecasting and screening items. Asian Journal of Research in Business Economics and Management, 5(2), 130-143. https://doi.org/10.5958/2249-7307.2015.00036.5
Henseler, J., Hubona, G., & Ray, P. A. (2016). Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: updated guidelines. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 116(1), 2-20. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-09-2015-0382
Jalalion, N., & Farsijani, H. (2020). Identifying strategies and ranking lean production tools for achieving world-class production using fuzzy grey theory. Journal of Business Strategies, 17(16), 79-98. https://cs.shahed.ac.ir/article_3419.html
Khodadadi Pour, M., Davoodi, D., & Davoodi, S. M. R. (2023). Random cross-efficiency in evaluating decision-making units with undesirable factors. Quarterly Journal of Quantitative Studies in Management, 14(4), 71-97. https://sanad.iau.ir/fa/Journal/qrm/Article/935033
Mahmoudi, M., & Mahmoud Oghati, S. (2021). Optimal placement of switches and distributed generation resources in power distribution networks using fuzzy membership functions. Iranian Society of Fuzzy Systems, 4(1), 79-110. https://www.sid.ir/paper/1040650/fa
Parsa Rad, A., & Azizi, A. (2021). Lean approach: Necessary or sufficient? Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Challenges and Innovative Solutions in Industrial Engineering, Management, and Accounting PAPER NO - 1244574,
Pourabadolahankooch, M., Nowbahar, E., Sajoodi, S., & Khalafi, R. (2021). Efficiency and scale: Evidence from electricity distribution companies in Iran. Iranian Journal of Energy Economics, 10(39), 71-97. https://jiee.atu.ac.ir/article_14274.html
Saffie, N. A. M., & Rasmani, K. A. (2016). Fuzzy delphimethod: Issues and challenges. 2016 International Conference on Logistics, Informatics and Service Sciences (LISS),
Sagarra, M., Mar-Molinero, C., & Agasisti, T. (2017). Exploring the efficiency of Mexican universities: Integrating data envelopment analysis and multidimensional scaling. Omega, 67, 123-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2016.04.006
Tanakian, M. J., Mehrjou, M., & Nofresti, S. (2021). Criteria for selecting wireless telecommunications technology for the smart grid measurement system in Iran. Iranian Journal of Quality and Productivity in Electrical Industry, 10(3), 48-61. https://www.sid.ir/paper/966047/fa
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Roxana Radmaneshi (Author); Farhad Hadinejad; Hasan Farsigani (Translator)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









