Development of a Mathematical Model Based on Ordered Load for Production and Assembly Line Balancing
Keywords:
Assembly line balancing, Ordered load, Mathematical optimization, Heuristic algorithm, Production efficiency, Demand variabilityAbstract
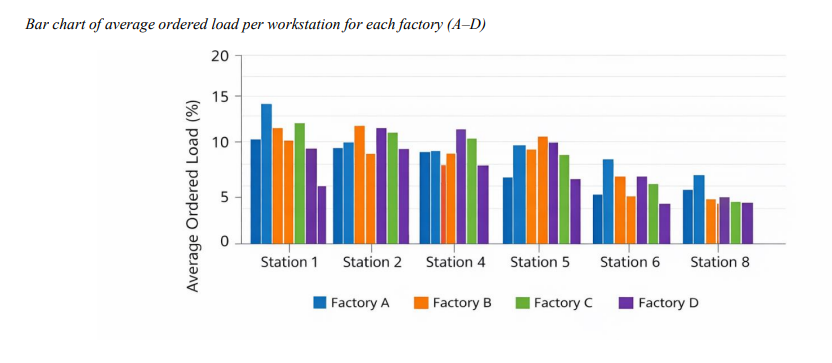
This study aims to develop and validate a mathematical assembly line balancing model based on ordered load to improve workload equity, reduce idle time, and enhance productivity in order-driven production environments. The study adopted an applied, quantitative research design using real operational data collected from multiple industrial production and assembly lines characterized by heterogeneous orders and mixed-model production. Ordered load was defined as the effective workload imposed on each workstation as a function of order quantity, product mix, and processing requirements. A mixed-integer mathematical programming model was formulated to minimize workload imbalance and idle time under precedence and capacity constraints. The model was solved using an exact optimization approach (Gurobi) to obtain benchmark solutions, and a heuristic algorithm implemented in MATLAB to address scalability and computational efficiency. Model validation was conducted through numerical experiments, cross-factory comparison, and sensitivity analysis under ±10% and ±20% ordered load variations. Exact optimization results showed substantial improvements in line balance index across all factories, accompanied by significant reductions in idle time and workload variance. Productivity increased consistently without additional resources, indicating more effective utilization of existing capacity. The heuristic algorithm achieved solution quality exceeding 97% of the exact optimum while reducing computation time by over 90%, demonstrating strong scalability. Sensitivity analysis confirmed that the model maintained stable balance performance under demand fluctuations, with mid-line stations identified as structurally critical but effectively controlled through load redistribution. The findings confirm that incorporating ordered load into assembly line balancing provides a more realistic and robust representation of demand-driven workload, leading to superior balance, efficiency, and adaptability compared to traditional time-based approaches.
References
Akpinar, M. E. (2022). A Linear Physical Programming Model for Assembly Line Balancing Problem. Journal of Engineering Research, 10(1), 316-329. https://doi.org/10.36909/jer.12711
Aufy, S. A., & Kassam, A. H. (2020). A Consecutive Heuristic Algorithm for Balancing a Mixed - Model Assembly Line Type II Using a (W-Tawh) Model Developed for Straight and U-Shaped Layouts. Iop Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, 671(1), 012147. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/671/1/012147
Aufy, S. A., Kassam, A. H., & Ismeal, G. A. (2021). Examining Rebalancing Considers of the Mixed-Model Assembly Line Type-Ii for the Straight and U-Shaped Layout Using the Taguchi Method. Engineering and Technology Journal, 39(2A), 280-294. https://doi.org/10.30684/etj.v39i2a.1740
Belkharroubi, L., & Yahyaoui, K. (2021). A Hybrid Grasp-Genetic Algorithm for Mixed-Model Assembly Line Balancing Problem Type 2. International Journal of Computing, 424-432. https://doi.org/10.47839/ijc.20.3.2289
Bongomin, O., Mwasiagi, J. I., Nganyi, E. O., & Nibikora, I. (2020a). A Complex Garment Assembly Line Balancing Using Simulation‐based Optimization. Engineering Reports, 2(11). https://doi.org/10.1002/eng2.12258
Bongomin, O., Mwasiagi, J. I., Nganyi, E. O., & Nibikora, I. (2020b). Improvement of Garment Assembly Line Efficiency Using Line Balancing Technique. Engineering Reports, 2(4). https://doi.org/10.1002/eng2.12157
Breznik, M., Buchmeister, B., & Herzog, N. V. (2023). Assembly Line Optimization Using MTM Time Standard and Simulation Modeling—A Case Study. Applied Sciences, 13(10), 6265. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13106265
Dang, Z., & Xie, N. (2023). Assembly Line Balancing and Capacity Evaluation Based on Interval Grey Processing Time. Grey Systems Theory and Application, 14(2), 374-395. https://doi.org/10.1108/gs-09-2023-0084
Duah, E., Pakmoni, L., & Appiah-Kubi, E. (2025). Green human resource management and organizational efficiency among local assemblies: role of process innovation and knowledge sharing. Journal of Organizational Effectiveness: People and Performance, 12(1), 168-190. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOEPP-11-2023-0511
Fani, V., Bindi, B., & Bandinelli, R. (2020). Balancing Assembly Line in the Footwear Industry Using Simulation: A Case Study. 56-62. https://doi.org/10.7148/2020-0056
Gulivindala, A. K., Bahubalendruni, M. V. A. R., Varupala, S. S. V. P., & Sankaranarayanasamy, K. (2020). A Heuristic Method With a Novel Stability Concept to Perform Parallel Assembly Sequence Planning by Subassembly Detection. Assembly Automation, 40(5), 779-787. https://doi.org/10.1108/aa-01-2020-0017
Hoa, N. T. X., Hai, A. V., & Quang, A. N. (2023). Applying Genetic Algorithm for Line Balancing Problem in Garment Manufacture. 203-220. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6463-150-0_15
Jia, G., Zhang, Y., Shen, S., Liu, B., Hu, X., & Wu, C. (2023). Load Balancing of Two-Sided Assembly Line Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Applied Sciences, 13(13), 7439. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13137439
Jiang, L. (2023). Design Optimization of Material Distribution for Mixed Model Assembly Line Based on Production Scheduling Sequence. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2671275
Jiao, Y., Cao, N., Li, J., Li, L., & Deng, X. (2022). Balancing a U-Shaped Assembly Line With a Heuristic Algorithm Based on a Comprehensive Rank Value. Sustainability, 14(2), 775. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14020775
Jiao, Y., Deng, X., Li, M., Xing, X.-c., & Xu, B. (2021). Balancing of Parallel U-Shaped Assembly Lines With a Heuristic Algorithm Based on Bidirectional Priority Values. Concurrent Engineering, 30(1), 80-92. https://doi.org/10.1177/1063293x211065506
Kharuddin, M. H., Ramli, M. F., & Masran, M. H. (2020). Line Balancing Using Heuristic Procedure and Simulation of Assembly Line. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, 17(2), 774. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v17.i2.pp774-782
Legesse, A., Tesfaye, E., & Berhan, E. (2020). Multi-Objective Optimization of Mixed Model Assembly Line Balancing in an Assemble-to-Order Industry With Stochastic Environment. International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 12(3), 90-107. https://doi.org/10.4314/ijest.v12i3.9
Mumcu, Y. K. (2022). Application of Heuristic Assembly Line Balancing Methods to Lighting Automation Industry. European Journal of Technic, 12(2), 204-208. https://doi.org/10.36222/ejt.1191203
Rahman, H. F., Janardhanan, M. N., & Nielsen, P. (2020). An Integrated Approach for Line Balancing and AGV Scheduling Towards Smart Assembly Systems. Assembly Automation, 40(2), 219-234. https://doi.org/10.1108/aa-03-2019-0057
Ramli, A. N., & Mohd Fadzil Faisae Ab, R. (2021). A Review of Assembly Line Balancing Optimisation With Energy Consideration Using Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 236(5), 475-485. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544054211040612
Sarhadi, E. (2026). Examining the Effect of Theory of Constraints on Reducing Normal and Abnormal Waste in Tire Manufacturing Companies. Strategic Management Accounting Quarterly, 2(1), 54-69. https://www.smajournal.ir/article_220043_en.html
Sotskov, Y. N. (2023). Assembly and Production Line Designing, Balancing and Scheduling With Inaccurate Data: A Survey and Perspectives. Algorithms, 16(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/a16020100
Sun, B., & Wang, L. (2020). An Estimation of Distribution Algorithm With Branch-and-Bound Based Knowledge for Robotic Assembly Line Balancing. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 7(3), 1125-1138. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-020-00166-z
Wang, X., Wu, W., Xing, Z., Zhang, T., & Niu, H. (2023). A Look-Ahead AGV Scheduling Algorithm With Processing Sequence Conflict-Free for a No-Buffer Assembly Line. Journal of Advanced Mechanical Design Systems and Manufacturing, 17(5), JAMDSM0063-JAMDSM0063. https://doi.org/10.1299/jamdsm.2023jamdsm0063
Wang, Y., & Wu, Z. (2020). Digital Twin-Based Production Scheduling System for Heavy Truck Frame Shop. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part C Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 236(4), 1931-1942. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406220913306
Weckenborg, C., Kieckhäfer, K., Müller, C., Grunewald, M., & Spengler, T. (2019). Balancing of Assembly Lines With Collaborative Robots. Bur - Business Research, 13(1), 93-132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40685-019-0101-y
Xia, B., Li, Y., Gu, J., & Peng, Y. (2024). Research on Sustainable Scheduling of Material-Handling Systems in Mixed-Model Assembly Workshops Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Sustainability, 16(22), 10025. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162210025
Xia, B., Zhang, M., Gao, Y., Yang, J., & Peng, Y. (2023). Design for Optimally Routing and Scheduling a Tow Train for Just-in-Time Material Supply of Mixed-Model Assembly Lines. Sustainability, 15(19), 14567. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151914567
Yan, H. S., & Wan, X.-Q. (2022). Self-Reconfiguration and Rescheduling of Aero-Engine Assembly Shop With Rework Disruption in Knowledgeable Manufacturing Environment. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 237(8), 1230-1240. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544054221123470
Yue, L., Chen, Y., Mumtaz, J., & Ullah, S. (2021). Dynamic Mixed Model Lotsizing and Scheduling for Flexible Machining Lines Using a Constructive Heuristic. Processes, 9(7), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9071255
Zhang, X. (2021). Automated Fist Assembly Line Design. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-885688/v1
Zhang, Y., Mai, H., Luo, J., Qiao, H., & Liu, P. (2023). Material Consumption Smoothing for Mixed-Model Assembly Lines Using an Improved Target Tracking Method. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 2562(1), 012047. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2562/1/012047
Zhao, R., Zou, G., Su, Q., Zou, S., Deng, W., Yu, A., & Zhang, H. (2022). Digital Twins-Based Production Line Design and Simulation Optimization of Large-Scale Mobile Phone Assembly Workshop. Machines, 10(5), 367. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10050367
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Behzad Bararzadeh (Author); Alireza Irajpour; Reza Ehtesham Rasi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









