Testing the Human Resource Allocation Model with a Soft Skills Approach in Knowledge-Based Companies
Keywords:
Human Resources, Human Resource Allocation, Soft SkillsAbstract
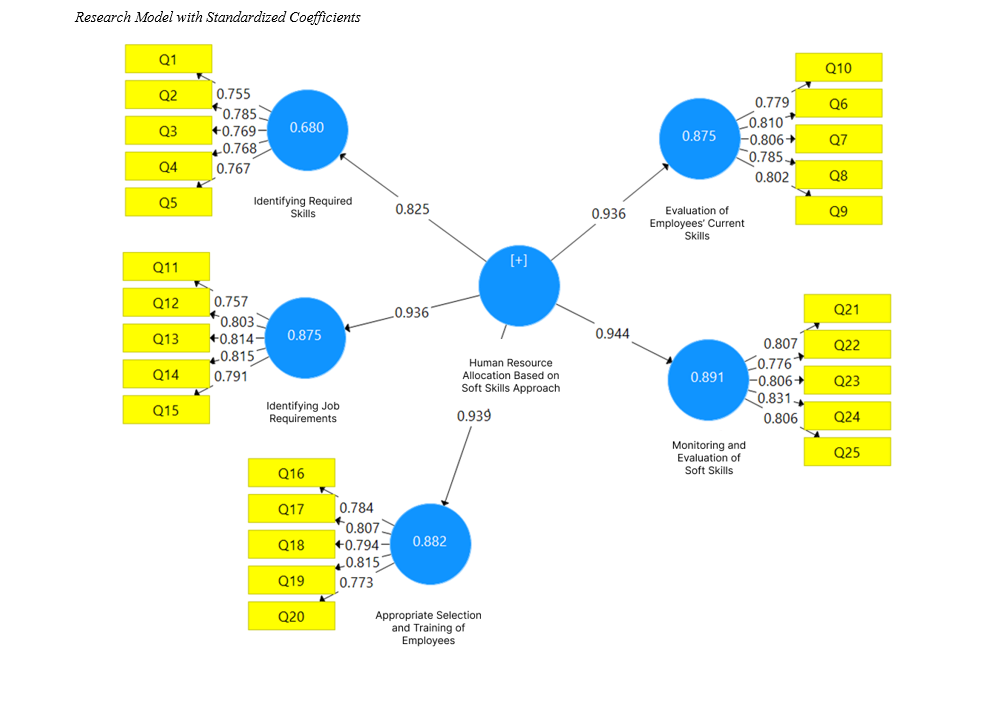
This study aimed to design and validate a human resource allocation model based on a soft skills approach in knowledge-based companies operating in Iraq. The research employed an applied, quantitative, and descriptive-correlational design. The statistical population consisted of employees working in knowledge-based companies across Iraq. Given the infinite size of the population, the sample size was determined to be 384 using Cochran’s formula. Data were collected through a researcher-made questionnaire designed to capture various dimensions and indicators related to soft skills in human resource management. The constructs included identifying required skills, assessing current employee skills, identifying job requirements, appropriate selection and training, and monitoring and evaluating soft skills. Data analysis was conducted using structural equation modeling (SEM) with SmartPLS software, and model fit was evaluated using the GOF index. The results indicated that all hypothesized relationships within the model were statistically significant (t > 1.96). Specifically, human resource allocation based on soft skills showed strong and significant relationships with: evaluation of current employee skills (t = 175.84; factor loading = 0.93), appropriate selection and training of employees (t = 196.219; factor loading = 0.93), identification of required skills (t = 49.372; factor loading = 0.82), identification of job requirements (t = 197.961; factor loading = 0.93), and monitoring and evaluating soft skills (t = 222.504; factor loading = 0.94). The overall model demonstrated a strong fit with a GOF value of 0.67. The findings highlight the strategic role of soft skills in effective human resource allocation. Organizations can enhance employee performance and organizational alignment by investing in identifying, developing, and assessing soft skills. Training programs, continuous feedback, and cross-functional project participation are recommended to improve soft skill capacities. This model provides a robust framework for integrating soft skills into HR strategies in knowledge-based environments.
References
Aprilita, K. P., & Pritasari, A. (2024). The Influence of Soft Skills Development on Perceived Work Readiness: Case of Recent Public University Graduates. Jurnal Ekonomi, Manajemen, Bisnis, dan Sosial (EMBISS), 4(4), 291-310. https://embiss.com/index.php/embiss/article/view/327
Bahuguna, P. C., Srivastava, R., & Tiwari, S. (2024). Human resources analytics: where do we go from here? Benchmarking: An International Journal, 31(2), 640-668. https://doi.org/10.1108/BIJ-06-2022-0401
Barani. (2020). Analyzing the Position of Technical and Vocational Education and Training in the Comprehensive Scientific Map of the Country. Karafen Scientific Quarterly, 16(2). https://karafan.nus.ac.ir/article_105070.html
Black, P. V., & Esch. (2020). Ai-enabled recruiting: What is it and how should a manager use it? Business Horizons, 63(2), 215-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bushor.2019.12.001
Bruno, Z., Haselein, J., & Silva, C. d. (2022). A knowledge‐based system for electric motors compliance verification in a multinational‐level company. Expert Systems. https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12979
Dewa, I., & Satrya, G. (2023). International Journal of Business, Economics and Social Development Assistance in Demographic Administration Innovation in Surabaya. International Journal of Business, Economics and Social Development, 4(2), 60-63. https://doi.org/10.46336/ijbesd.v4i2.438
Falaha, M. A., Saadon, M. S. I., & Othman, M. R. (2023). THE EFFECT OF STRATEGIC ORGANIZATIONAL CHALLENGES ON MANAGING HUMAN RESOURCES THE JORDAN SME LOGISTIC COMPANIES. Russian Law Journal, 11(4S), 321-337. https://doi.org/10.52783/rlj.v11i4s.855
Fernández-Sanz, J., Gómez-Pérez, A., & Castillo, M. (2017). E-skills match: A framework for mapping and integrating the main skills, knowledge and competence standards and models for ICT occupations. Computers Standards & Interfaces, 51, 30-42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csi.2016.11.004
Gkrimpizi, V., & Peristeras, I. (2023). Classification of Barriers to Digital Transformation in Higher Education Institutions: Systematic Literature Review. Education Sciences, 13(7), 746. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13070746
Khalagh Khah, N. H. (2021). The Role of Scientific-Technology Literacy of Educational Managers in Increasing Soft Skills Components. Bi-Monthly Scientific-Research Journal: A New Approach in Educational Management, 11(46). https://jedu.marvdasht.iau.ir/article_4549.html?lang=en
Kolak, A., Soltani, M. S., & Mohammadi Bagheri, N. (2023). The Impact of Human Resource Management on Organizational Performance from the Perspectives of Managers and Employees with a Comparative Approach. Quarterly Journal of Human Resource Education and Improvement, 10(1), 40-63. https://journals.iau.ir/article_704780.html
Martins, H., Rouco, C., Piedade, L., & Borba, F. (2020). Soft skills for hard times: Developing a preparedness framework for overcoming crises in higher education students. Proceedings of the International Conference on Intellectual Capital, Knowledge Management and Organisational Learning, ICICKM,
Marzuki, S. N., Muljan, M., Haslinda, H., & Affandi, L. (2024). Soft Skill and Hard Skill Development Model in Improving the Quality of Human Resources in the Higher Education Environment. QALAMUNA: Jurnal Pendidikan, Sosial, dan Agama, 16(1), 571-582. https://doi.org/10.37680/qalamuna.v16i1.5070
Rahimi, S., & Sohili, R. (2023). Investigating the Status of Soft Skills Among Librarians in University Libraries of Kermanshah Province. University Library and Information Research. https://jlib.ut.ac.ir/article_93651.html?lang=en
Sopa, M., Asbari, A., Purwanto, P. B., Santoso, D. H., Mustofa, S., & Maesaroh, R. (2020). Hard skills versus soft skills: Which are more important for Indonesian employees' innovation capability. International Journal of Control and Automation, 13(2), 156-175.
Sukarno, M. S., Riadi, S., & Kurnia, I. (2024). Implementation of Regional Development Planning Policies at the Regional Development Planning Agency of Central Sulawesi Province: Study on the Preparation of the (2024) Central Sulawesi Provincial Government Work Plan. LAW&PASS: International Journal of Law, Public Administration and Social Studies, 1(2), 81-91. https://lawpass.org/index.php/ojs/article/view/9
Thimmanna, G., & Bhat. (2022). A study on challenges in human resource management. Multidisciplinary Journal for Applied Research in Engineering and Technology. https://doi.org/10.54228/mjaret07220005
Timourzadeh, F., & Najafi, H. (2021). The Influence and Perception of Soft Skills on Critical Thinking and Innovative Behavior of School Managers (With a DEMATEL Methodological Approach). Quarterly Journal of Advanced Education, 1(3). https://journals.iau.ir/article_691393.html
Vu, H. D., & Ho, T. T. (2020). Provincial foreign direct investment absorptive capacity of Vietnam. Entrepreneurial Business and Economics Review, 8(2), 7-26. https://doi.org/10.15678/EBER.2020.080201
Wang, X. L., & Zheng. (2018). A knowledge-guided multi-objective fruit fly optimization algorithm for the multi-skill resource constrained project scheduling problem. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 38, 54-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.swevo.2017.06.001
Wijan, P. (2012). How to develop learning for the 21st Century Students. Sodsri-Saridwong Foundation. https://jedu.marvdasht.iau.ir/m/article_2965.html?lang=en
Zaid Najy Shawash, M. A. A.-A. A. M. A.-Z. (2023). The Role of Soft Skills in Job Performance: A Field Study in the Yemeni Public Telecommunications Corporation. Oman University Journal, 3(6).
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Abbas Owaid Abdulhussein Jebur (Author); Sayed Hamidreza Mirtavousi; Mustafa Sabah Hlaihel Almaliki, Saeid Aghasi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









