Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience through Correlation-Aware Risk Prioritization: A Comparative and Statistical Analysis Approach
Keywords:
Supply chain risk management, DEMATEL, Petri Net, Neural networks, Risk prioritization, Automotive industryAbstract
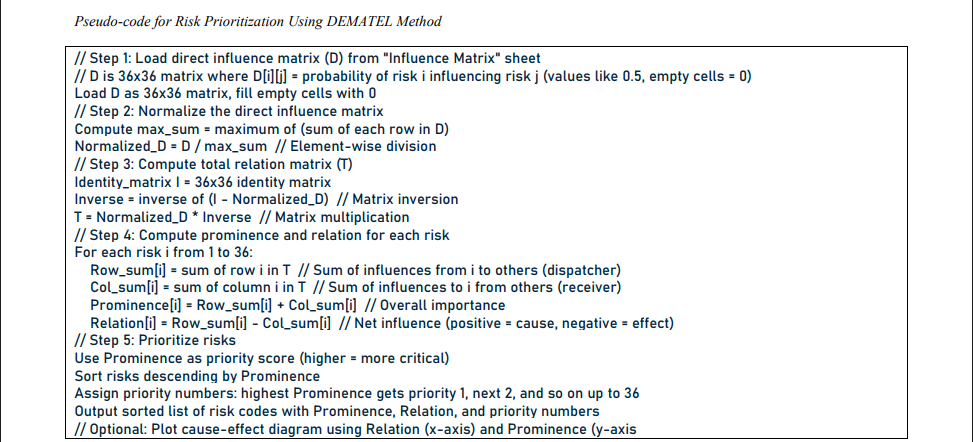
In today’s interconnected automotive supply chains, managing correlated risks is critical to prevent cascading disruptions. This study compares four prioritization methodologies—Risk Priority Number (RPN), Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL), Petri Net simulation, and a feedforward multilayer perceptron (MLP) neural network—applied to 36 expert-identified risks within vehicle component supply chains. Using severity, occurrence, and correlation-based influence data, the methods reveal contrasting prioritization patterns. While RPN assumes risk independence, DEMATEL and Petri Net capture causal propagation, and the MLP model identifies non-linear relationships among risks. Statistical tests (Friedman and post-hoc Wilcoxon) confirm significant differences, showing that correlation-aware approaches alter risk rankings by 15–25%. Applied to Saipa Press’s heavy stamping component supply chain under sanctions and regulatory constraints, the proposed framework improves resource allocation and highlights systemic vulnerabilities. The results advocate hybrid, correlation-integrated approaches for resilient supply chain decision-making in volatile environments.
References
Asad, R., & Khan, M. (2023). Risk assessment in automotive supply chains: A fuzzy DEMATEL approach. International Journal of Production Research, 61(5), 1456-1472. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2022.2144978
Chatterjee, P., & Chakraborty, S. (2022). An intuitionistic fuzzy DEMATEL-integrated COPRAS method for evaluating green suppliers in an Indian automotive manufacturing organization. Soft Computing, 26(4), 1803-1821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06668-7
Chen, J., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Dynamic risk assessment in automotive supply chains using colored Petri Nets. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 34(2), 567-582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-021-01845-7
Choudhary, N. A., Singh, S., Schoenherr, T., & Ramkumar, M. (2022). Risk assessment in supply chains: a state-of-the-art review of methodologies and their applications. Annals of Operations Research, 322, 565-607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04700-9
Deng, X., & Hu, Y. (2022). Identifying and analyzing barriers to circular supply chain implementation using fuzzy DEMATEL. Journal of Cleaner Production, 338, 130554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130554
Diakoulakis, K., & Kechagias, E. (2023). DEMATEL-ISM integration for risk analysis in manufacturing supply chains: An empirical study. Procedia CIRP, 119, 1023-1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2023.03.078
Ebrahimi, S., & Ghahari, A. (2022). Risk assessment in agricultural supply chains using interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy DEMATEL. Soft Computing, 26(12), 5678-5694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-022-06934-5
Emrouznejad, A., Abbasi, S., & Sıcakyüz, C. (2023). Supply chain risk management: A content analysis-based review of existing and emerging topics. Supply Chain Analytics, 3(4), 100031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sca.2023.100031
Fan, D., & Lo, C. K. Y. (2023). Behavioural operations management in supply chains: A review and future research directions. International Journal of Production Research, 61(10), 3456-3478. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2022.2057345
Govindan, K., & Panneer Selvam, A. K. (2022). Sustainable supply chain management in the automotive industry: A fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 29, 456-472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.11.015
Han, J., & Zhang, Y. (2023). Stochastic Petri Nets for supplier risk assessment in automotive manufacturing. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 229, 108912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2022.108912
Jahan, N., & Sarker, R. (2022). Timed Petri Nets for modeling recovery times in disrupted supply chains. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 165, 107923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2022.107923
Jahin, M. A., Naife, S. A., Saha, A. K., & Mridha, M. F. (2023). AI in supply chain risk assessment: A systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis. https://arxiv.org/html/2401.10895v2
Kaur, H., & Singh, S. P. (2023). A robust decision-making approach for sustainable supply chain risk mitigation in emerging markets. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 180, 109333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2023.109333
Li, X., & Wang, Y. (2024). AI-driven disruption prediction using deep neural networks in supply chain risk management. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 190, 109933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2024.109933
Li, Y., & Zhang, X. (2023). Colored Petri Nets for emergency supply chain management: A COVID-19 case study. Omega, 112, 102745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2022.102745
Liang, D., Bhamra, R., Liu, Z., & Pan, Y. (2022). Risk Propagation and Supply Chain Health Control Based on the SIR Epidemic Model. Mathematics, 10(16), 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10163008
Mangla, S. K., Luthra, S., Jakhar, S. K., & Tyagi, M. (2023). Petri Net-based modeling of blockchain adoption in sustainable supply chains. Annals of Operations Research, 319(1), 123-145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-022-04567-8
Mangla, S. K., Sharma, S. K., & Kazançoğlu, Y. (2022). Risk management in sustainable supply chains: A systematic literature review. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 33, 1023-1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.07.012
Mastrogiacomo, L., & O'Kane, C. (2023). Operational risk modeling using generalized stochastic Petri Nets in manufacturing systems. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 67, 234-248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2023.01.005
Mousavi, S. M., & Haji, R. (2024). Integrating DEMATEL-ISM and neural network models for supply chain risk prioritization. Expert Systems with Applications, 242, 122948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122948
Singh, A. K., & Kumar, P. (2022). RPN-based failure mode prioritization in automotive component manufacturing: An Indian perspective. Quality & Reliability Engineering International, 38(3), 1234-1248. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.3012
Sun, L., & Yu, H. (2023). Neural network approaches for supply chain risk prediction: A comparative study. Expert Systems with Applications, 212, 118678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.118678
Tathavadekar, V. P. (2025). Sustainable and Resilient Supply Chain Practices through Digital Transformation and Circular Economy Strategies. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=5448394
Tobing, A. E. N., & Santosa, W. (2025). The Effect of Absorptive Capacity on Supply Chain Innovation Performance Through Supply Chain Resilience in Manufacturing Companies: Empirical Study From Bogor Region, Indonesia. Golden Ratio of Data in Summary, 5(1), 119-131. https://doi.org/10.52970/grdis.v5i1.927
Trivedi, A., & Jakhar, S. K. (2023). Multi-criteria decision-making methods for supply chain risk assessment: A comparative analysis. International Journal of Production Research, 61(8), 2567-2589. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2022.2057346
Vahdani, B., & Hadipour, H. (2022). A hybrid fuzzy MCDM approach for risk prioritization in automotive supply chains. Soft Computing, 26(5), 2345-2361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-021-06589-5
Wang, H., Chen, Y., Xie, J., & Liu, C. (2025). Research on Digital Empowerment, Innovation Vitality and Manufacturing Supply Chain Resilience Mechanism. PLoS One, 20(2), e0316183. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0316183
Wang, J., & Wang, X. (2023). Comparative analysis of neural networks and statistical methods for supply chain risk prediction. European Journal of Operational Research, 305(2), 789-804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2022.07.045
Wang, M., & Zhu, Q. (2022). Machine learning vs. traditional statistical methods in supply chain forecasting: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Forecasting, 38(3), 1123-1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijforecast.2021.09.008
Xu, J., & Zhang, L. (2023). Deep learning applications in supply chain risk management: A comprehensive review. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 175, 108856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2022.108856
Yang, Z., & Wang, Y. (2022). Neural networks for supply chain anomaly detection: A comparative study. Decision Support Systems, 152, 113678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dss.2021.113678
Yao, J. (2025). Analysis of the Factors Influencing Grain Supply Chain Resilience in China Using Bayesian Structural Equation Modeling. Sustainability, 17(7), 3250. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17073250
Yu, Y. (2025). The Impact of Digital Transformation on Supply Chain Resilience in Manufacturing: The Mediating Role of Supply Chain Integration. Sustainability, 17(9), 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17093873
Zammori, F., & Cavaliere, R. (2023). FMEA 2.0: A review of advanced approaches for failure mode prioritization. Quality & Reliability Engineering International, 39(1), 123-145. https://doi.org/10.1002/qre.3023
Zarei, M., & Ghasemi, A. (2025). Correlation-aware risk assessment in Iran's automotive supply chains under sanctions. International Journal of Production Economics, 259, 109982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2024.109982
Zhang, Q., & Wang, H. (2022). Deep learning for supply chain risk management: Applications and challenges. Annals of Operations Research, 308(1), 567-589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-021-04234-5
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Zohreh Mousavi (Author); Sadigh Raissi; Kambiz Jalali Farahani (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









