Application of Sandelowski and Barroso Technique in Identifying the Components of the Reliability Model of Green Value Chain Management in Manufacturing Industries
Keywords:
Reliability, Value Chain Management, Green Supply Chain, Manufacturing IndustriesAbstract
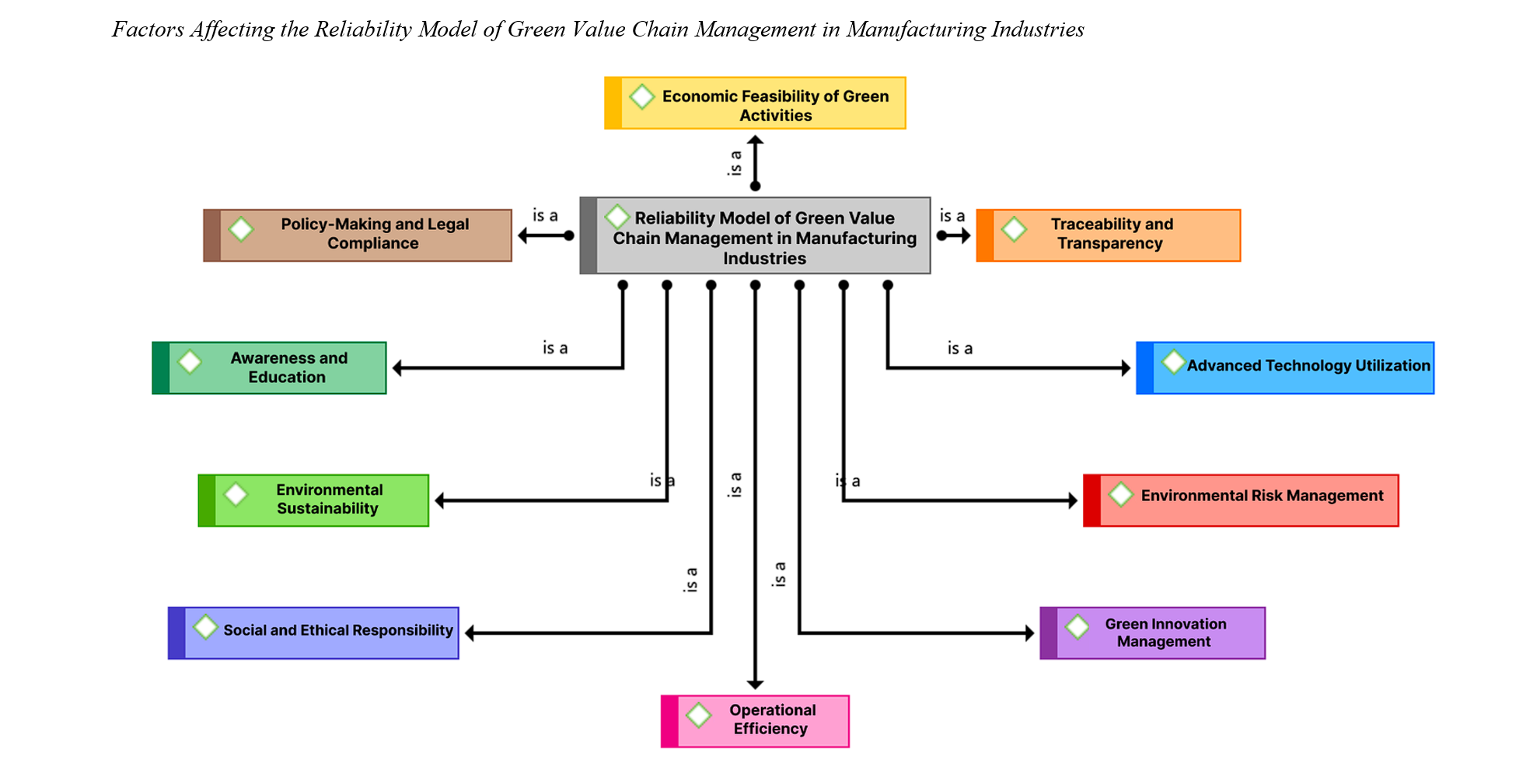
The aim of this research is to apply the Sandelowski and Barroso technique in identifying the components of the reliability model of green value chain management in manufacturing industries. The researcher employed a systematic review and meta-synthesis approach to analyze the results and findings of previous scholars. By implementing the seven steps of Sandelowski and Barroso’s method, the study identified influencing factors. Out of 282 articles, 36 were selected based on the CASP method. The validity of the analysis was confirmed with a Kappa coefficient of 0.747. To measure reliability and ensure quality control, the transcription method was used, which indicated an excellent level of agreement for the identified indicators. Data analysis was conducted using MAXQDA software, leading to the identification of 40 primary concepts based on 40 indicators grouped into 10 categories. Based on the meta-synthesis technique, 10 dimensions were categorized from these concepts. In addition, 10 concepts and 40 indicators were identified. The 10 dimensions are: environmental sustainability, operational efficiency, social and ethical responsibility, green innovation management, traceability and transparency, environmental risk management, awareness-raising and education, policymaking and regulatory compliance, utilization of advanced technologies, and economic viability of green activities. These models must be designed in such a way that they simultaneously address environmental, social, and economic needs. By focusing on these dimensions, manufacturing industries can not only enhance the reliability of their value chain but also contribute to achieving sustainable development goals through the creation of sustainable value. Thus, the use of these models can play a key role in increasing the resilience of manufacturing industries against environmental and economic challenges.
References
Almeida, R. P., Ayala, N. F., Benitez, G. B., Kliemann Neto, F. J., & Frank, A. G. (2022). How to assess investments in Industry 4.0 technologies? A multiple-criteria framework for economic, financial, and sociotechnical factors. Production Planning & Control, 1-20. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537287.2022.2035445
Bagheri, M., & Javadian, N. (2022). Presenting a Model for Optimizing a Multi-Echelon Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Iran University of Science and Technology]. Tehran.
Dang, C., Wang, F., Yang, Z., Zhang, H., & Qian, Y. (2022). Evaluating and forecasting the risks of small to medium-sized enterprises in the supply chain finance market using blockchain technology and deep learning model. Operations Management Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12063-021-00252-6
Hu, W., & Tresirichod, T. (2024). Impact of Green Entrepreneurial Orientation on Sustainable Performance: The Mediating Role of Green Intellectual Capital and Green Supply Chain Management. Asian Administration & Management Review, 7(1). https://so01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/AAMR/article/view/272653
Jafari Eskandari, M., & Emami Salout, H. (2022). A Multi-Objective Optimization Model for Risk Assessment in a Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Under Parameter Uncertainty: Using the Conditional Value at Risk (CVaR) Approach. Industrial Management Studies, 20(66), 251-298. https://jims.atu.ac.ir/article_11435.html?lang=en
Jiang, Y., Zhang, Y., Yeganeh, A. J., & Zhao, D. (2024). Resilience of Green Building Supply Chain: Capabilities, Risks and Influence Mechanism. Journal of Green Building, 19(3), 41-69. https://doi.org/10.3992/jgb.19.3.41
Judijanto, L., Utami, E. Y., & Harsono, I. (2024). Green Supply Chain Finance: A Bibliometric Review of Financing Instruments, Challenges, and Opportunities. West Science Interdisciplinary Studies, 2(03), 647-655. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsis.v2i03.745
Kazancoglu, Y., Yuksel, D., & Sezer, M. (2022). A Green Dual-Channel Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Design Model. Journal of Cleaner Production, 332, 130062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130062
Kumar, S., Sigroha, M., Kumar, K., & Sarkar, B. (2022). Manufacturing/remanufacturing based supply chain management under advertisements and carbon emissions Process. RAIRO-Operations Research, 56, 831-851. https://doi.org/10.1051/ro/2021189
Lerman, L. V., Benitez, G. B., Müller, J. M., de Sousa, P. R., & Frank, A. G. (2022). Smart green supply chain management: a configurational approach to enhance green performance through digital transformation. Supply chain management, 27(7), 147-176. https://doi.org/10.1108/SCM-02-2022-0059
Liao, F., Hu, Y., Chen, M., & Xu, S. (2024). Digital transformation and corporate green supply chain efficiency: Evidence from China. Economic Analysis and Policy, 81, 195-207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eap.2023.11.033
Nayal, K., Raut, R. D., Yadav, V. S., Priyadarshinee, P., & Narkhede, B. E. (2022). The impact of sustainable development strategy on sustainable supply chain firm performance in the digital transformation era. Business Strategy and the Environment, 31, 845-859. https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.2921
Ningrum, E., Nugroho, A., Darmansyah, D., & Ahmar, N. (2024). A Scoping Review of Green Supply Chain and Company Performance. International Journal of Quantitative Research and Modeling, 5, 26-30. https://doi.org/10.46336/ijqrm.v5i1.608
Piao, G., & Xiao, B. (2023). Analyzing the Effectiveness of Finance in Supply Chain in Solving the Financing Difficulties of SMEs Based on Grey Theory Model. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2022, 7608937. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7608937
Rachid, B., Roland, D., Sebastien, D., & Ivana, R. (2024). Risk Management Approach for Lean, Agile, Resilient and Green Supply Chain. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, International Journal of Social, Behavioral, Educational, Economic, Business and Industrial Engineering, 11(4), 742-750. https://publications.waset.org/10006688/risk-management-approach-for-lean-agile-resilient-and-green-supply-chain
Ramezani, M., Mahdavi, I., & Babaei, E. (2022). A New Model for Designing a Resilient-Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Mazandaran University of Science and Technology].
Rashid, A., Baloch, N., Rasheed, R., & Ngah, A. H. (2024). Big data analytics-artificial intelligence and sustainable performance through green supply chain practices in manufacturing firms of a developing country. Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management.
Saadi, E., Fathi Hafshejani, K., & Radfar, R. (2022). Designing a Multi-Objective Mathematical Model for a Closed-Loop Supply Chain with a Supplier Selection Approach and Consideration of Discounts. Engineering Management and Soft Computing, 7(2), 73-113. https://www.magiran.com/paper/2270155/designing-a-multi-objective-closed-loop-supply-chain-mathematical-model-with-supplier-selection-approach-and-considering-discount?lang=en
Seyed Nejad Fahim, S. R. (2024). Analyzing the Role of Strategic Management Accounting in Sustainable Supply Chain Management (Case Study: Food Manufacturing Companies in Gilan Province). Green Development Management Studies.
Shahriari, M., & Gholami, M. (2022). Competition in Collecting Returned Products Between Manufacturer and Retailer Under Greening and Quality Improvement of Products in a Closed-Loop Supply Chain. Production and Operations Management, 13(3), 137-158. https://jpom.ui.ac.ir/article_26927.html?lang=en
Soon, A., Heidari, A., Khalilzadeh, M., Antucheviciene, J., Zavadskas, E. K., & Zahedi, F. (2022). Multi-Objective Sustainable Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Design Considering Multiple Products with Different Quality Levels. Systems, 10(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems10040094
Yu, W., Chavez, R., Feng, M., & Wiengarten, F. (2024). Integrated green supply chain management and operational performance. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 19(5/6), 683-696.
Zadeh, K., Harsej, F., Sadeghpour, M., & Molani Aghdam, M. (2023). Designing a multi-echelon closed-loop supply chain with disruption in the distribution centers under uncertainty. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 19(4), 2582-2615. https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2022057
Zhang, R. (2024). Methods for Carbon Reduction Through Green Supply Chain Management in the Automotive Industry. Frontiers in Business Economics and Management, 17(3), 301-303. https://doi.org/10.54097/s5vaf884
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Arash Rafati (Author); Hasan Mehrmanesh; Ahmadreza Kasraee (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.









